- Platforms
- Foundations
-
Patterns
- Overview
- Accessing private data
- Charting data
- Collaboration and sharing
- Drag and drop
- Entering data
- Feedback
- File management
- Going full screen
- Launching
- Live-viewing apps
- Loading
- Managing accounts
- Managing notifications
- Modality
- Multitasking
- Offering help
- Onboarding
- Playing audio
- Playing haptics
- Playing video
- Printing
- Ratings and reviews
- Searching
- Settings
- Undo and redo
- Workouts
-
Components
- All components
- Content
- Layout and organization
- Menus and actions
- Navigation and search
- Presentation
- Selection and input
- Status
- System experiences
- Inputs
-
Technologies
- All technologies
- AirPlay
- Always On
- App Clips
- Apple Pay
- Augmented reality
- CareKit
- CarPlay
- Game Center
- HealthKit
- HomeKit
- iCloud
- ID Verifier
- In-app purchase
- Live Photos
- Mac Catalyst
- Machine learning
- Maps
- Messages for Business
- NFC
- Photo editing
- ResearchKit
- SharePlay
- ShazamKit
- Sign in with Apple
- Siri
- Tap to Pay on iPhone
- Wallet
CarPlay
iPhone apps that appear on the car’s built-in display are optimized for the driving environment and meet the unique demands of the car.


The best apps support brief interactions and never command the driver’s attention. On-screen information is minimal, relevant, and requires little decision making. Voice interaction using Siri enables drivers to control many apps without taking their hands off the steering wheel or eyes off the road. Well-known iOS paradigms, including interface elements, icons, text appearance, and terminology provide a familiar, intuitive experience.
iPhone apps like Maps, Messages, Music, and Phone display car-appropriate interfaces that look great in CarPlay and are easy to operate while driving. The audio app, automaker app, messaging app, or Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) app you design should be just as simple and easy to operate.
Audio apps
Apps that serve audio content (audiobooks, Internet radio, news, podcasts, and sports, for example) can expose that content through the car’s built-in display. These apps supply an app icon for the CarPlay Home screen (in addition to a corresponding app icon on the iPhone Home screen); a hierarchical list of content to display in a tabbed browser; and information for a Now Playing screen. The system presents this information in an interface optimized for CarPlay, using a template that resembles the Music app. Although your app's basic appearance is handled by the system, there are still many design considerations for ensuring a great user experience.
For developer guidance, see CarPlay and MediaPlayer.
Structuring and providing data
Audio apps must provide a complete navigable hierarchy of audio information—radio stations, albums, artists, titles, and so forth. The system uses this information to populate tabs and tables in the CarPlay interface, and to respond to user actions like track selection and media playback.
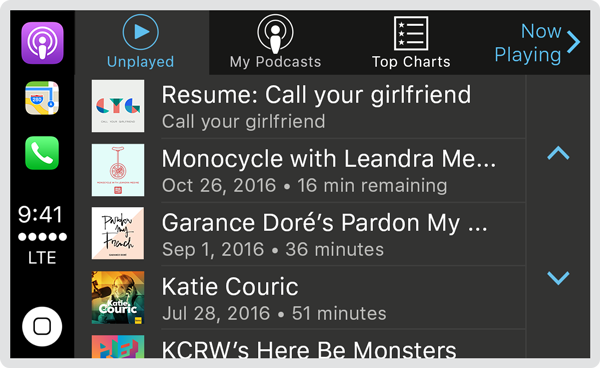
Always provide content, even when data is unavailable. Drivers occasionally encounter poor network reception. If data is unavailable, provide placeholder or cached content so the system can still generate the interface for your app. Supply updated content once it becomes available.
Limit your content hierarchy to three levels or fewer. The less navigation required to reach content, the better. Although the system permits a maximum depth of five levels, three levels or fewer is recommended. For example, Artists > Albums > Songs, or Playlists > Songs.
Use multiple tabs to organize content and ease navigation. The tab bar at the top of the screen flattens your app’s hierarchy and lets the user quickly switch between different categories of content.
Show the most relevant content first. Anticipate information and actions most important to the driver, and present it first to reduce scrolling and navigation. Music, for example, prioritizes recently added music and playlists, and presents them at the top of the first tab. In Podcasts, the top of the first tab lets you instantly pause or resume the active episode.
Include single-touch playback actions at the top level of your hierarchy. Easy one-touch playback options such as Shuffle and Resume add value and convenience to your app.
Intelligently filter content when the vehicle is moving. Certain cars may cause CarPlay to truncate lists of content when the vehicle is in motion or has exceeded a certain speed. Consider displaying a curated set of essential information and options when this mode becomes active.
Supply succinct titles and descriptions. Always include a title, like an album name or track name. If it makes sense, provide a subtitle with additional information, such as the artist or composer name. Keep titles and subtitles short so they can be scanned quickly and peripherally.
Provide supplementary artwork. Imagery appearing in the navigation hierarchy, such as album art, improves the appearance of your app and makes content easier to locate at a glance.
![]()
Denote explicit content. CarPlay displays an indicator when content is marked as explicit, making it easy for people to detect and skip.
![]()
Denote streaming content. CarPlay displays an indicator when content is marked as streaming. Some users have cellular data usage limits, so be mindful when streaming content over the cellular network.
Don't require sign in or configuration steps in CarPlay. Audio apps in CarPlay are about consumption. Don't ask the user to perform setup steps on the car's display. It's highly probable your app will be launched on iPhone before it's used in CarPlay, so your iPhone experience should ensure setup is complete. If a setup step does become necessary in CarPlay, gracefully handle the situation without encouraging the user to pick up their phone. For example, consider offering cached audio the user can play without signing in.
For developer guidance, see MPPlayableContentDataSource.
Playing media
The system automatically shows a Now Playing screen when playing audio content, and populates it with the data your app provides.
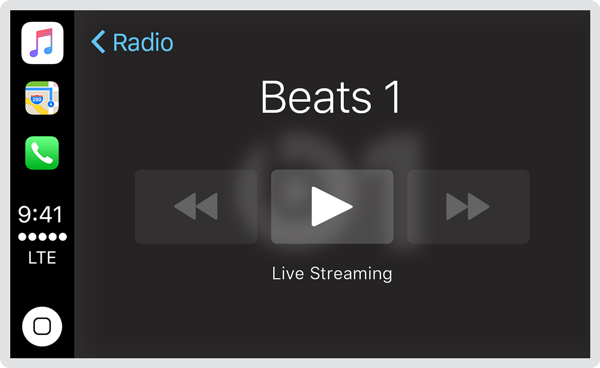
Provide useful, accurate information and controls when playing audio. The Now Playing screen can show a title, artist, album art, rating, and playback progress. It can also include controls for liking, disliking, and bookmarking the playing audio. Information should be updated whenever playback begins and ends.
Don’t redefine the meaning of playback controls. A physical Play button in the car, for example, should begin playing audio, not skip to the next track.
Resume audio playback when appropriate after an interruption. Temporary interruptions like incoming phone calls are resumable. Permanent interruptions, like a music playlist initiated by Siri, are nonresumable. When a resumable interruption occurs, your app should resume playback when the interruption ends if audio was actively playing when the interruption started. An app that is not playing audio when an interruption occurs has nothing to resume.
For developer guidance, see MPPlayableContentDelegate and MPNowPlayingInfoCenter.
Automaker apps
Automakers can design custom apps that provide information, expose useful functionality, and control built-in vehicle features—like climate controls, GPS, and the radio—without leaving the CarPlay experience.
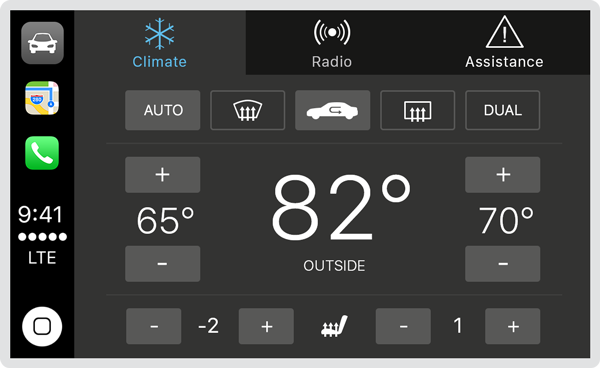
Limit controls and content to what's relevant in the car. Exposing every feature of your iPhone app through CarPlay can make your app more complex and less safe to use while driving. Don’t offer features that aren’t useful to drivers.
Prefer standard controls. A subset of system-provided user interface controls are optimized for CarPlay, including buttons, labels, navigation bars, tab bars, and tables. See System elements. Displaying interface controls that don't match the visual style of other CarPlay apps can result in a fragmented and confusing user experience.
Avoid redesigning standard controls. The system-provided controls offer consistency and are optimized for legibility and interactivity in the car. If you must design custom versions of standard controls, make sure they’re similar in appearance to standard CarPlay controls, and large enough to see and interact with while driving.
Never mimic the design of the car's native interface. Your app should have the familiar look and feel of other CarPlay apps.
For related guidance, see Visual design.
Messaging and VoIP apps
Messaging and VoIP apps use Siri and are exclusively voice-driven. They don’t present interfaces to the user, so no interface design is necessary that’s specific to CarPlay.
Support both reading and composing messages. A messaging app optimized for CarPlay must allow the user to read and compose messages using only their voice.
Enable CarPlay notifications. A messaging app must explicitly opt in for its notifications to appear in CarPlay. For developer guidance, see UNNotificationCategoryOptionAllowInCarPlay.
Display only message notifications. Categorize your messaging notifications in a way that segregates them from other types of notifications.
Enable the appropriate Siri functions if your app supports VoIP. To work with CarPlay, a VoIP app must allow the user to search the call history and start audio calls using Siri. For developer guidance, see INSearchCallHistoryIntentIdentifier, and INStartAudioCallIntentIdentifier.